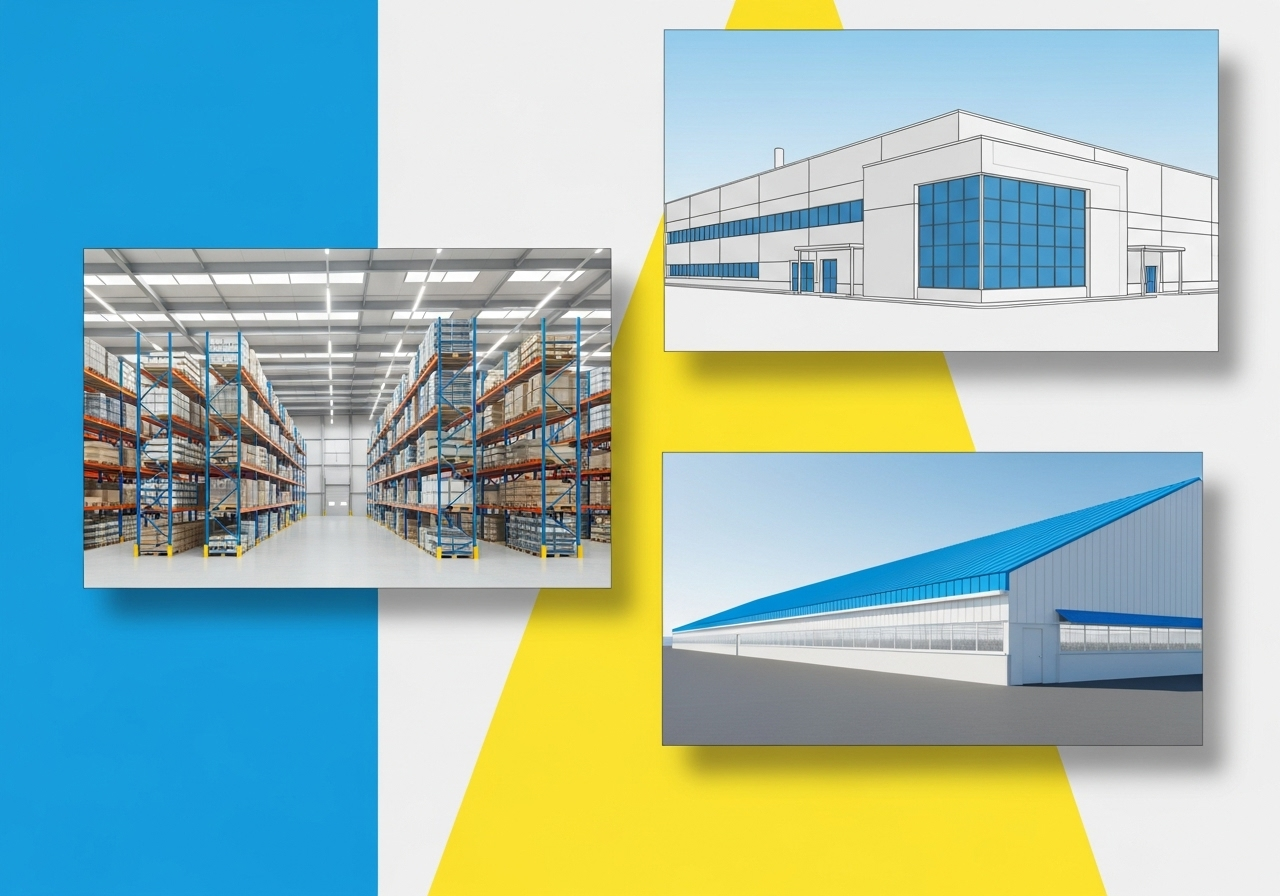
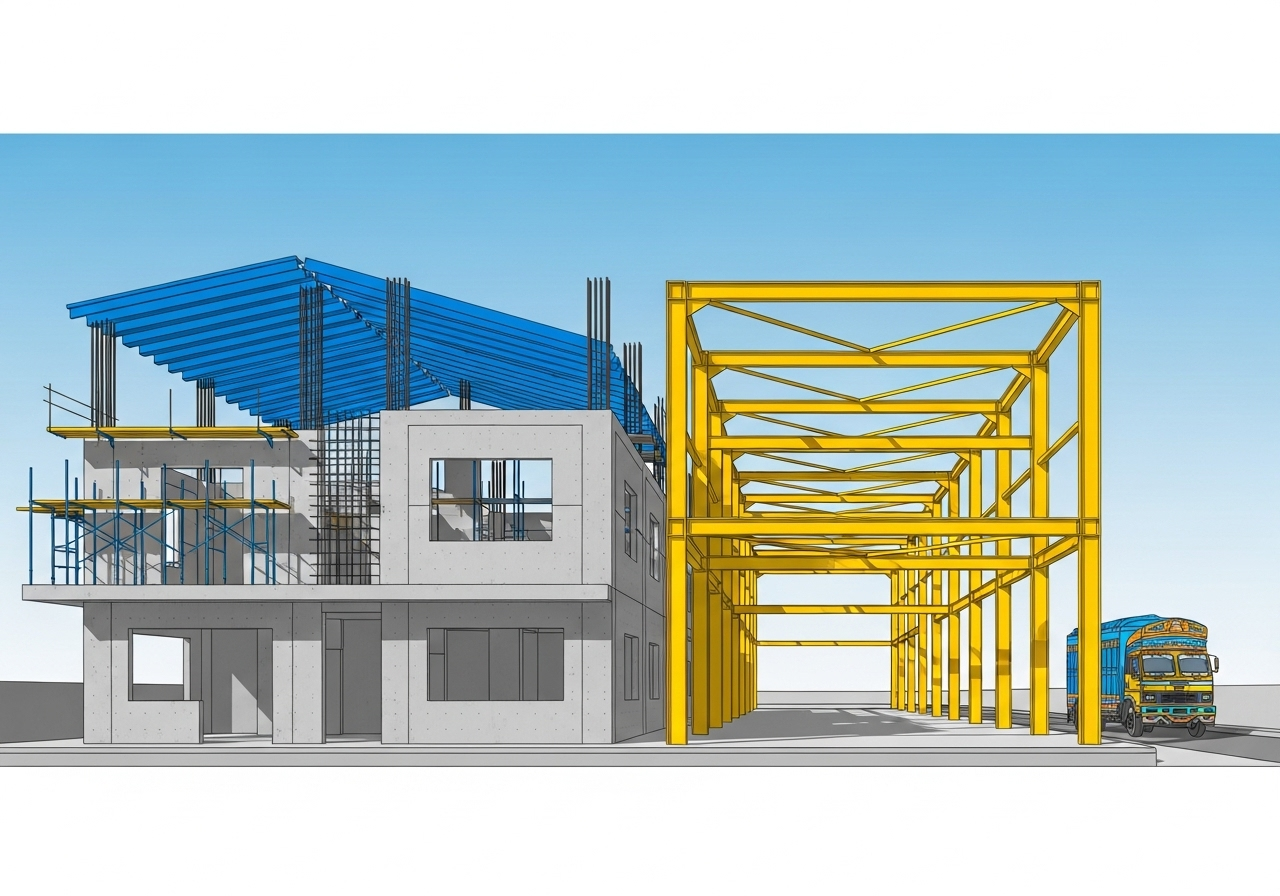
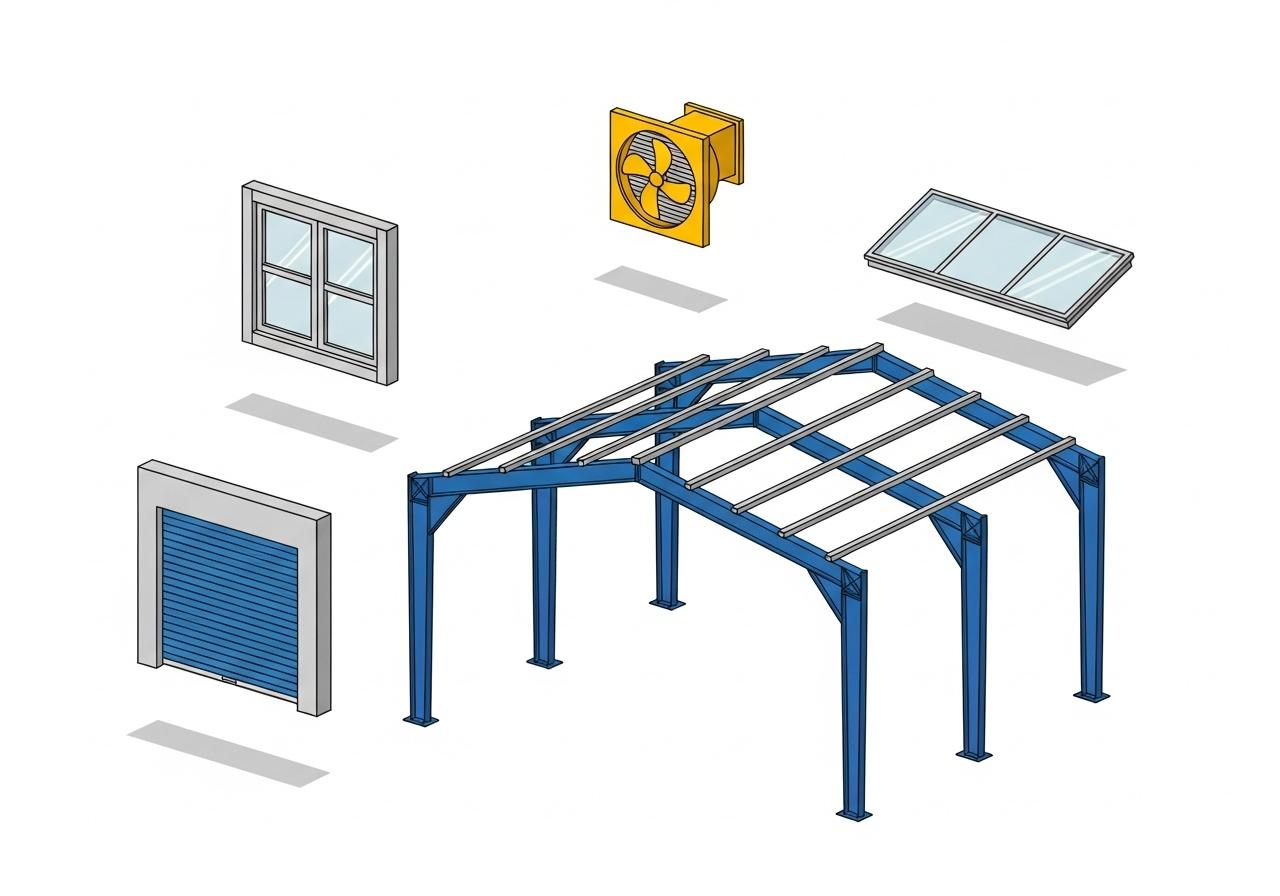
PEB stands for Pre-Engineered Building. It is a construction method where the building’s structural components are designed and manufactured in a factory, off-site. These components are then transported to the construction location and assembled. This approach is different from traditional construction, where most of the fabrication and building happens directly on the project site. The entire system is engineered to work together from the start.
What is a Pre-Engineered Building (PEB)?
A Pre-Engineered Building is a complete steel-framed building system. The key is that the design and engineering happen before any manufacturing begins. Using specialized software, engineers design the entire structure to meet specific dimensions, local building codes, and load requirements (like wind and snow). This detailed planning allows for the optimization of steel usage, which reduces weight and cost. The result is a structure where every component is made to fit perfectly with the others.
The Core Components of a PEB System
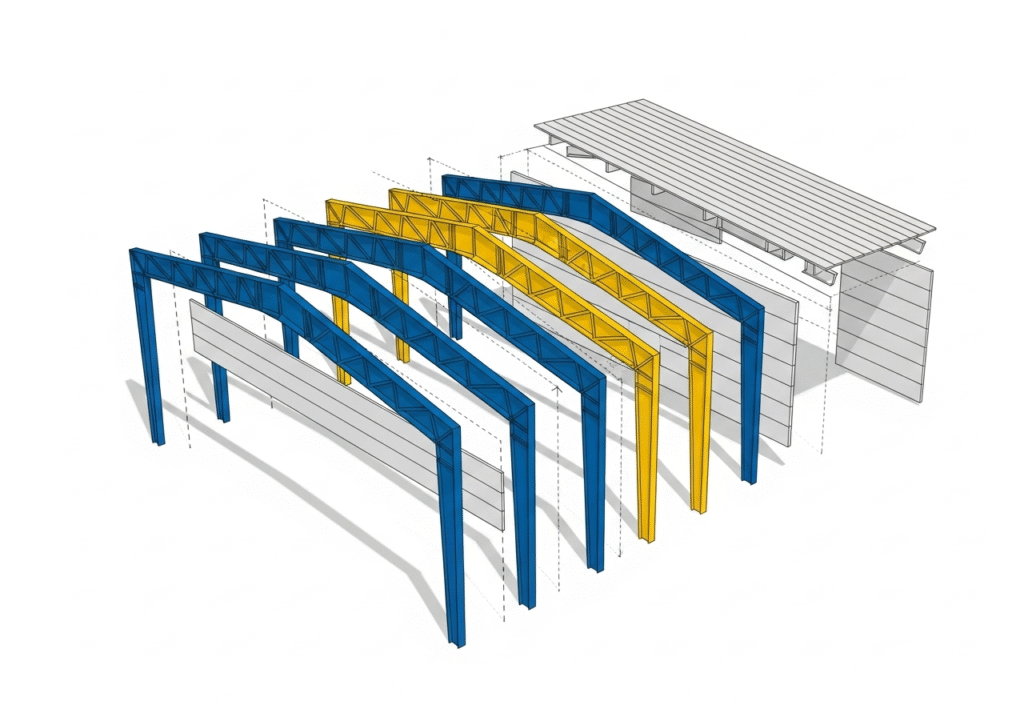
A PEB system has three main types of components. First are the primary frames. These are the main steel skeletons of the building, typically I-beams that form the columns and roof rafters. They bear the main load of the structure. Second are the secondary structural members. These include parts like purlins and girts, which are smaller steel components that span between the primary frames. They support the roof and wall sheeting and transfer loads to the main frame. Third is the roof and wall cladding. This is the outer skin of the building, usually made of metal sheets, which provides weather protection.
How is a PEB Constructed?
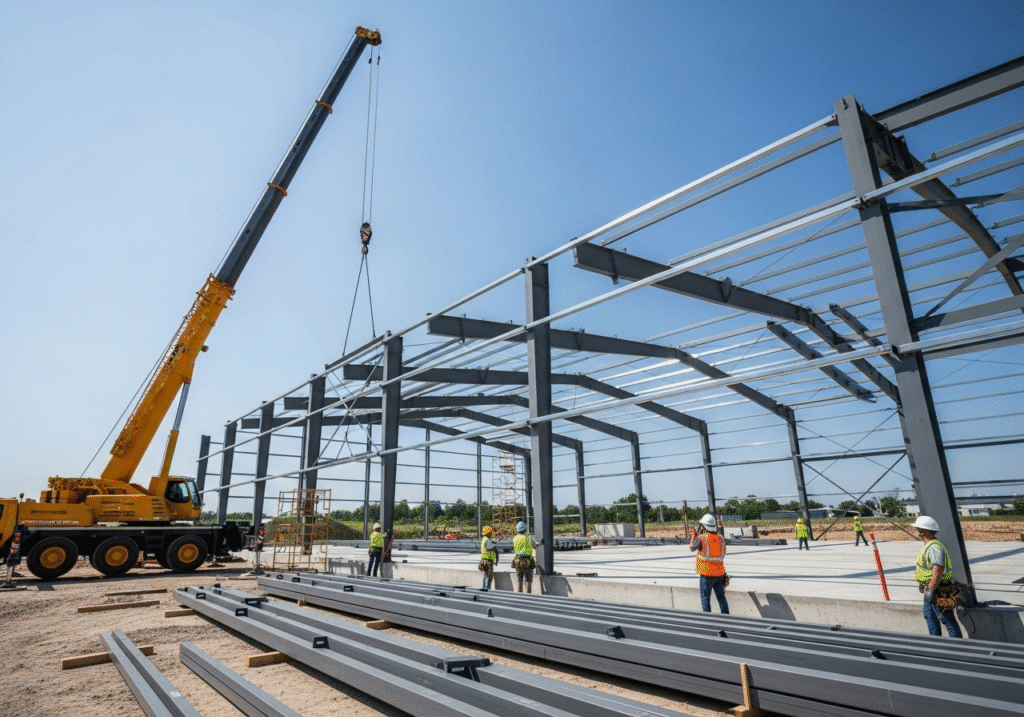
The process begins with the design and engineering phase. Once the client approves the final drawings, the fabrication starts in the factory. Each component—every beam, column, and purlin—is cut, welded, and painted according to the precise specifications. After a quality check, the complete building kit is shipped to the site. The on-site work involves assembling these pre-made parts. The primary frames are erected first, followed by the secondary members, and finally, the cladding is attached. It is more of an assembly process than traditional construction.
Why Choose PEB over Traditional Construction?
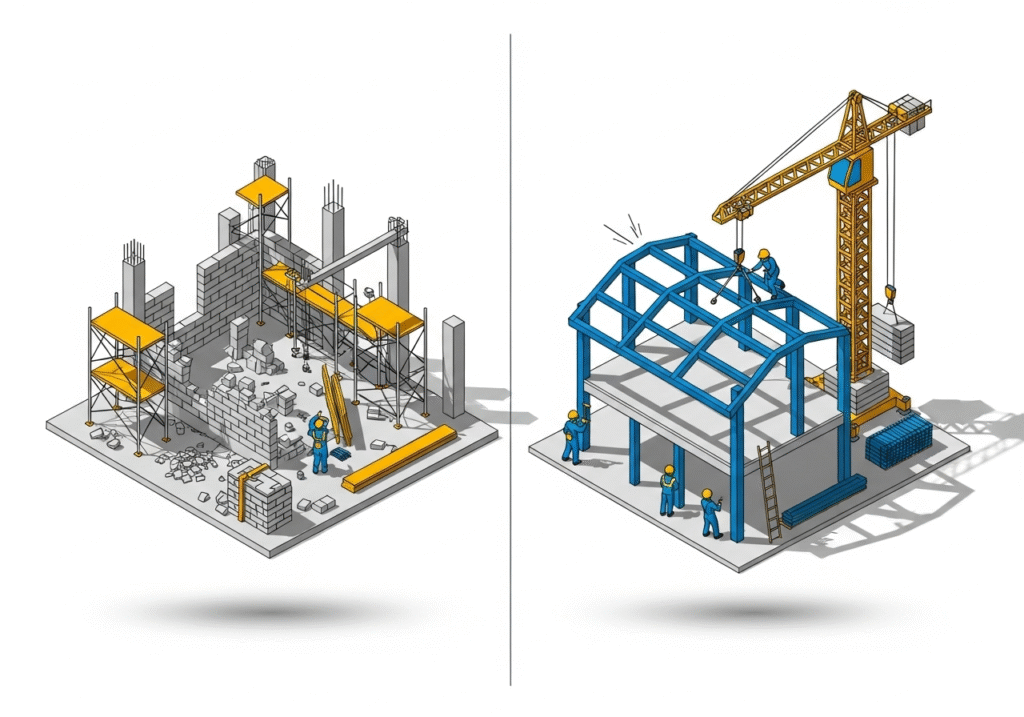
The main advantage of PEB is speed. Because the components are made in a controlled factory environment while the site foundation is being prepared, the total project time can be cut by as much as 30-50%. Cost is another factor. The optimized design uses less steel, and faster assembly requires less on-site labor, leading to savings. Design flexibility is also a benefit. PEB systems can create very large, clear-span interiors without needing support columns, which is ideal for many industrial and commercial uses.
Common Applications for PEB Structures
You see pre-engineered buildings everywhere. They are a common choice for warehouses and large distribution centers because of the need for wide, open interior spaces. Factories and industrial workshops also use this method to accommodate large machinery and production lines. Other applications include poultry and dairy farm sheds, event halls, petrol station canopies, and even portable office cabins.
A Modern Approach to Building
Ultimately, PEB is a modern construction method that uses factory precision to deliver buildings quickly and economically. By handling the complex fabrication in a controlled setting, it simplifies the on-site work to an assembly process, reducing project timelines and potential errors.